Know more about Copyright: Copying the works of others ain’t a right
In today’s world, everyone seems to be in-touch with the cyberspace- a place where everything dwells in a virtual space. It’s a big world out there and people will fight for their own intellectual properties.As mentioned, intellectual properties are not limited to physical works such as books, but it now extends to works seen online. Furthermore, as copyright laws took into effect, a lot of companies filed bankruptcy due to copyright infringement. Even placing copyrighted photos on your own website may be considered a case of infringement.
As a startup, there is no room for ignorance on copyright and trademark. One wrong move and this may lead you to extinction. The fact that copyright laws vary in each country makes the thought of bankruptcy a lot scarier.
There’s just a lot of things to know about copyright and trademark and mind you, there’s just a thin hairline separating the differences between the two.
Copyright vs. trademark
Think of copyright as a tag on an intellectual work which says “This is mine.” A copyright gives the creator or an author the title of his own work. This includes published and unpublished original works may it be in a form of music, photo, novels, articles, literary works to name a few.
On the other hand, trademark is still a tag but this is more specific to profit- driven organizations.
Oftentimes,trademark is termed as a “servicemark”
, this is used by companies for their own identification.
Where do both ends meet? In copyright, what is protected is the form of expression and not the subject matter of the work itself. As an example, think of a startup offering a laundry service. Here the description, manner and system (how it works) can be copyrighted but this does not limit other startups to offer a laundry service. The same thought goes for trademarks.
Trademarks are used for a company’s identification, but this does not limit other companies to sell the same goods, and offer the same services as the former does.
Copyrights are registered by the Copyright Office of the Library of Congress. On the other hand, trademarks are registered in the United States Patent and Trademark Office.
Copyright Act 1976 and Digital Millennium Copyright Act
Indeed, the cyberspace has a lot of things to offer, but the restrictions and limitations in reproducing or copying a work seems too vague for many. More and more individuals now have the ability to reproduce works to any form possible however, chances are high that they are unaware whether what they are doing is a case of copyright infringement or not.Before the occurrence of internet boom, Copyright Act was already enacted in USA in the year 1976. In a nutshell, the 1976 Copyright Act criminalizes the reproduction and misuse of works, making infringement a crime. Copyright infringement happens when an act is done “wilfully and for purposes of commercial advantage or private financial gain.”
Penalties are set for copyright infringement as shown below:
Thanks to continuous innovations on technology; it is undeniable that piracy has grown over the years because reproduction became easier than before. Digital Millennium Copyright Act is similar to Copyright Act but more specific on digital works.
Even giant companies go to court due to copyright issues. For one, Viacom, the 6th largest broadcasting and cable company, sued Youtube and its corporate parent Google. After the ruling of the case was released in 2013, Youtube kept a close eye on infringed videos.
Role of World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
America is one of the 188 member states of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). WIPO is the global forum for intellectual property services, policy, information and cooperation. In addition, WIPO has established WIPOnet, a global information network that seeks to link over 300 intellectual property offices (IP offices) in all WIPO Member States. You can learn more about foreighn trademarks by registering a Trademark in the UAE to Protect Your Business.
Fair Use and “exceptions”
As the saying goes, “Every rule has an exception” and this holds true this time.
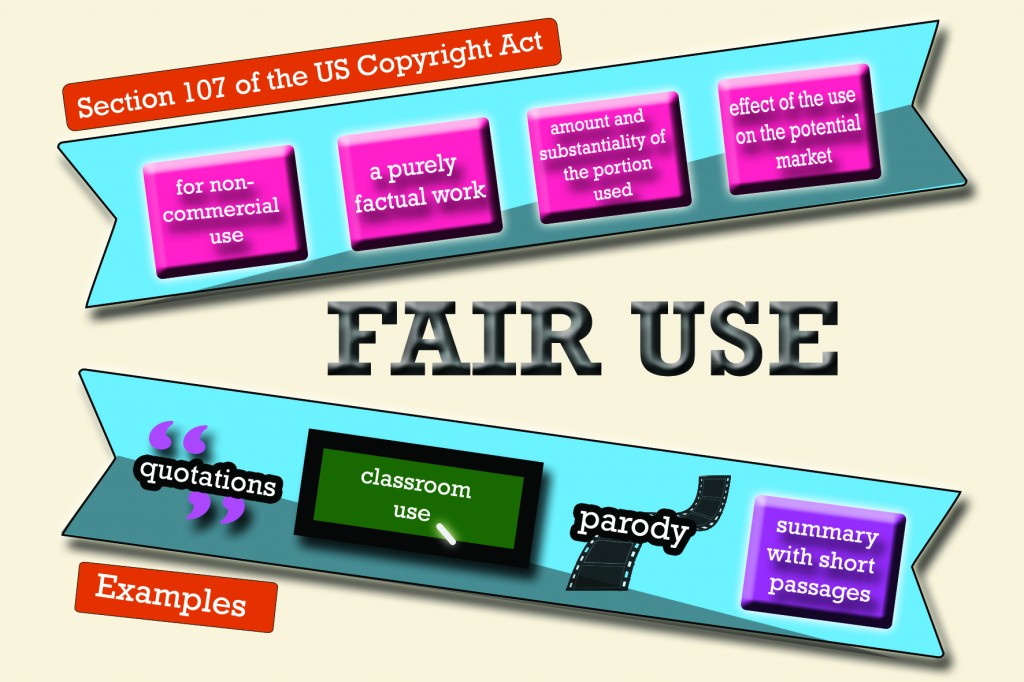
For the copyright law in USA, fair use is the exception.
When sued in court due to copyright infringement, fair use can be a form of legal defense. Proving your situation as a fair use case may be hard as its analysis is conducted on a case- to- case basis but, it is still important to take note of its 4 pillars as mentioned in Section 107 of the Copyright Act.
In the realm of licensing, the Creative Commons (CC) provides room for exception. CC is an NGO which aims to facilitate the legal sharing of creative works. It provides a number of copyright license options to the public, free of charge. These licenses allow copyright holders to define conditions under which others may use a work and to specify what types of use are acceptable. As of writing, there are over 882 million CC- licensed works and the numbers just grow over time.
There are also cases when works are made available to the public although, it must be emphasized that the public does not own it. These works are termed as public domain.
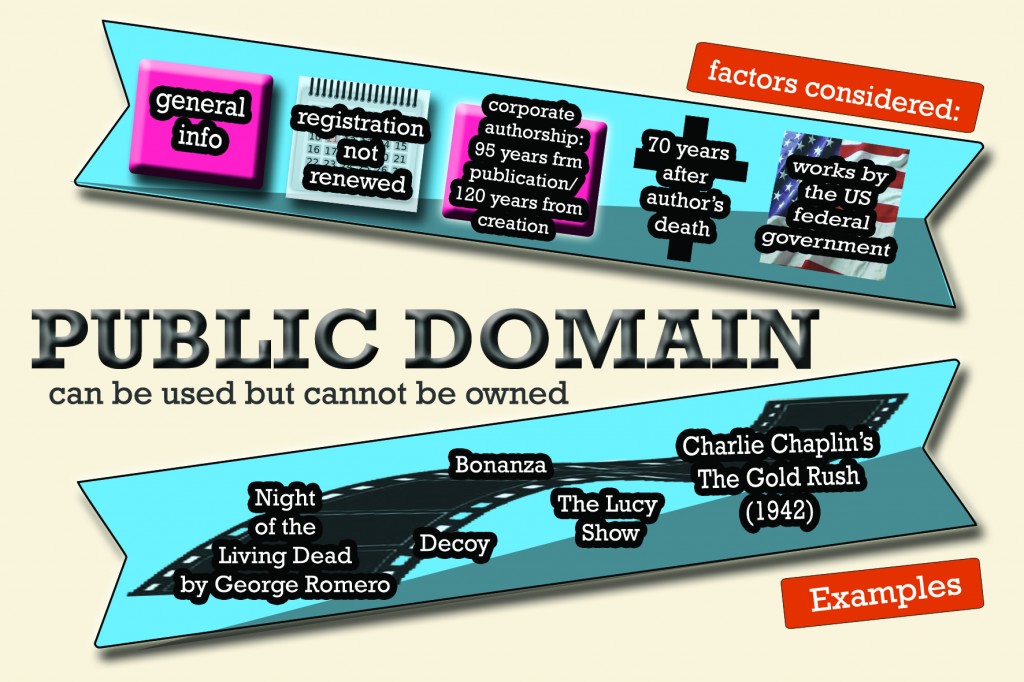
In the end, even if exceptions on copyright exist, caution is still needed. It is important to read a content’s terms of use, and note that just because a copyright is not displayed on their website does not mean you can copy it right away. In using intellectual properties especially those that are digital, caution is needed, and ignorance must be eliminated.
