List and Comparison of Business Structures
Deciding to start your own business and become an entrepreneur is a big decision. You may already have a great business idea and decided on the industry to venture into. You’re fired up and full of enthusiasm to begin your entrepreneurial journey. Least likely to enter your mind is the fact that you should also decide on the right structure applicable to your business.
Choosing a business structure will either make or break your first few years as a budding businessman. And it is these first few years that is considered the most crucial part of the life of a business.
Business structure defines the complexity of your business organization. It either helps or limits your ability to raise funds and capital. It may subject you to or shield you from federal duties and taxes. Most importantly, it will either protect your personal assets from creditors or legally give them the right to go after you.
These factors make the choice of a business structure a critical phase of business startups.
Contents
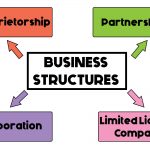
The most common structures that make up businesses today are: (1) Proprietorship; (2) Partnership; (3) Corporation; and (4) Limited Liability Company (LLC). Familiarize yourself with the different types of business structures and decide for yourself which suits your business the most.
Proprietorship

A proprietary form of business is the least complex and the most manageable among the business structures. It is a business that is solely owned and run by an individual. It only consists of you being the owner and the staff in your employment.
Fast Decision Making. Decision-making is fastest in Proprietorship type of businesses since you run and operate the business by yourself. You have the sole authority over your business and its day-to-day operation. Although, you may get pieces of advice from partners, friends and clients, or consult specialists from time to time, the decision- making in terms of running the business relies solely upon you.
Not Strictly Regulated. There is no formal action to be taken in becoming a proprietor other than the necessary permits and licenses required to register a business. The requirements for registering your business may vary depending on the state and type of industry.
No Income Tax. With regards to taxes, the earnings of the business go directly and wholly to the proprietor who will report the income in his or her Individual Income Tax Return or ITR, and pay the corresponding taxes.
Limited Capital. Capital will be limited to your own funding or savings and loans from banks and financing institutions.
Unlimited Liability. During closure of the business or worse, bankruptcy, business creditors are legally allowed to go after the personal assets of the proprietor in satisfying their claims. These personal assets will be given out to satisfy claims in this order: (1) government for duties and taxes unpaid; (2) creditors; (3) employees for unpaid wages if any.
The Proprietorship form of business is fit for small businesses which need less capital, less number of employees or none at all, and whose owner has the personal knowledge of the industry the business is into and will be hands- on in running and managing the business.
Partnership

The US Revised Uniform Partnership Act of 1994 define partnership as “an association of two or more persons to carry on as co-owners a business for profit”. This is the form of business owned by at least more than one but admission is only upon approval of all the other partners.
Partner’s Contribution and Share. Each partner will contribute either money, service or property for a business whose profits and losses will be shared among them.
Decision Making is Upon the Partners. It is among the partners to formulate an agreement on important issues like the proportion of profits and losses, the dispute settlement, and the dissolution of the partnership, among others. Decision making and all other activities to be undertaken by the business depends upon the agreement of the partners also.
Joint Liability. Each partner is jointly and individually liable for the decision made by all the other partners approved by the partnership agreement. Although, this agreement is not required by regulations to be in writing. It is advised that partnership agreement should be shown in public documents.
More Partners, More Capital. Funding and financing is relatively easier than sole proprietorship but still limited to the partners themselves.
No Strict Regulations. There are no particular applications required in forming a partnership other than choosing it as the business type in registering your business. Still, localities and industries vary in their requirements. An Annual Information Return has to be submitted to report profits, losses and all other significant transactions during the year.
No Income Taxes. In the US, partnerships do not pay income taxes for the business itself. The profits or loss is shared by the partners according to their agreement, and each partner is to report their share in their Individual Income Tax Returns and pay the taxes accordingly.
Individual Liabilities. The extent of liability of each partner depends upon the type of partner he or she is. There are two common types of partners whose presence also define the type of partnership:
General Partners – have unlimited liability. They are like the sole proprietors whose personal assets are up for claims by third parties upon liquidation. General partners form the general partnerships. General partnerships, unless stated in the partnership agreement, divides profits and losses equally among the partners.
Limited Partners – have limited liabilities only up to the extent of their contribution or investment. At least one limited partner in the partnership makes it a Limited Partnership. Creditors and other claimants cannot go after the assets of the limited partner other than his share in the partnership. Limited partners are likewise given limited chance to participate in business transactions, agreements, and decision-makings.
Lose a Partner, Partnership Dissolves. A special feature of the partnership form of business is that the change in the composition of its partners dissolves the partnership. Death, dismissal or withdrawal of at least one of the partners automatically results to dissolution. Dissolution of the partnership does not mean discontinuance of the business though. It is now upon the decision of the remaining partners to create a new partnership to continue the business. The business does not have to register again after the dissolution of the partnership, inclusion of the fact in the Annual Information Return is enough. The partners only have to create a new agreement for the new partnership.
Partnership form of business is best for businesses who offer services as their main source of income such as lawyers and accountants.
Corporation

Probably the most complex and sophisticated among all the business forms is the Corporation.
New Juridical Entity. It is a separate and new entity formed under the law of the state where it is registered. The ownership of Corporations is subdivided among its shareholders in the form of shares or stocks. It is the corporation who owns the business and not the stockholders. Rather, the stockholders form the corporation.
Ownership thru Stocks. These shares or stocks represent a residual interest in the corporation and are evidenced by stock certificates.
Corporate Officers. Stockholders elect the officers who will form the top management of the corporation. The officers will be responsible for the operations of the corporation and shall face the day- to- day decision making.
Decentralized Decision Making. Stockholders will be called for to participate in significant decision making occasions like declaration of dividends and any other events as declared in the Articles of Incorporation. This makes the decision making process in corporations difficult and not as easy and smooth sailing as the sole proprietorship or partnership.
Strict Regulations, More Documentation. A Corporation is basically formed upon registering with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
For registration, localities and industries vary in their requirements, but the most common include Articles of Incorporation, list of the corporate officers, and an accounting of stocks already sold and will be sold for public.
A corporation’s name sometimes is required to contain words like “Corporation”, “Incorporated”, “Corp.” or “Inc.”. Among all the other types of business structure, the Corporation is the most regulated form. The Corporation being a juridical entity has to submit periodic requirements in the continuance of its existence. All of its transactions must be fully documented to avoid federal and regulatory wraps.
Easier to Raise Capital. After registration of both the corporation and the business, the corporation may choose to sell its available stocks to the public.
In what is called “Initial Public Offering” or IPO, the public buys partial ownership of the corporation. This makes the ability of the corporation to raise capital easy and almost limitless.
Double Taxation. The major difference of a corporation compared to other forms of business structures is that the corporation itself is taxed for its earnings. A corporation submits its own tax return and pays its own taxes before distribution of net earnings to its shareholders in the form of dividends. The shareholders, upon receipt of the declared dividends, likewise report these dividends in their Individual Income Tax Returns and are again subjected to income tax, thus double taxation but in different form.
Board Resolution to Declare Dividends. Unlike sole proprietorships and partnerships which recognize and share profit respectively when they choose to, a corporation must approve a dividend declaration first before distributing its earnings. It is therefore a long way before a shareholder gets a taste of his or her booming business.
Limited Liability. Good thing in establishing a corporation as a business structure is that when it runs out of assets, there is nothing else to run after even the personal properties of its owners. Each stockholder is liable only to the extent of their investment.
Succession. Another advantage of a Corporation is that it can be considered immortal. Localities vary in the life span given to a corporation but are usually renewable, thus, making it possible for corporations to exist more than a hundred years. Unlike partnership, owners of a corporation can easily change from time to time without the approval of all the other stockholders. Some stockholders are even held private or use proxies in their place. (Talk about confidentiality!)
The corporation form of business is best fitted for large companies with a wide area of operation and a huge number of employees. This suits business ideas that need a huge sum of capital and financing.
Limited Liability Companies (LLC)

The newest and innovative legal structure for businesses today is the Limited Liability Company or LLCs. It is innovative in the sense that it uses the tax freeway and less regulatory benefits of a partnership yet enjoys the limited liability characteristic of a corporation. Not all states though allow the formation of an LLC. And for those who allow, there are also slight differences in the regulatory requirements and taxation but the basic features are never less the same.
Limited Liability. As stated already, owners, who are also called “members”, of an LLC, are liable only up to the extent of their investment to the company.
Less Regulatory Requirements. Record-keeping and documentation for LLCs is also not as cumbersome as a corporation. LLCs have their Articles of Organization which contain the basic information of the LLC and its members. Registration poses less hassle and less paperwork for LLCs. Articles of Organization are similar to that of Articles of Incorporation. LLCs should have the words “LLC” or “Limited Company” in its name. Check out this guide “limited vs unlimited company” to learn more.
Profit or Loss Sharing. Copying the features of a partnership, LLC members contribute money, service or properties to the business. Profits and losses are shared and distributed according to their agreement.
Taxes are Passed Through. An LLC is not a separate tax-paying entity, thus, taxes on its earnings are passed through to the members who pay the equivalent taxes of their share in the earnings of the LLC. Members report these earnings in their Individual Income Tax Return.
Dissolution like Partnerships. Dismissal, withdrawal or death of a member constitutes dissolution of the LLC. It is now up to the remaining members to create another LLC which will continue the business.Approval for an LLC legal structure varies among states. LLCs are taxed as corporations in some localities for specific business industries. Make sure to check with your State Office what legal structures are the possible options for your business.
Although, the legal structure of your business pose a critical aspect of your startup company, it is always reversible. Statutes allow the change of legal structure from one to another to cater the changing environment and needs of your business.
I made a summarized comparison table outlining the characteristics of the business structures in terms of organization, decision- making, capital, taxation, regulations, liability, best applicable to specific type of business, and dissolution or liquidation.
So feel free to upgrade to another structure if you feel your chosen structure doesn’t work out for your business. Just make sure to comply with all the regulatory requirements of the new business structure you will choose.
Now that you have been introduced to the different legal structures which your business may adopt, you should choose one which will fit and most applicable for your business. Consider the pros and cons of your chosen structure. Seek professional advice from experts in your field of industry, and in your locality, such as business consultants, local lawyers, accountant and seasoned entrepreneurs. Most importantly, be prepared, because, no matter the business structure, starting up and running your company will always be challenging. However, welcome the challenges, and choose wisely!
Sources:
US Small Business Administration
The Uniform Partnership Act (1997)
Tax Information for Businesses
Limited Partnership