Invoicing is a crucial part of any business, ensuring you get paid for your products or services. If you’re a business owner looking to streamline your invoicing process, you’ve come to the right place. Welcome to “Invoice 101: What, Why, How?”—your go-to guide for understanding and mastering the art of invoicing. We’ll break it down into easy steps so you can get your invoicing game on point.
Key Takeaways
How to write an invoice:
- Indicate the date of the transaction.
- Write the name of the client or customer.
- Fill up the specifics: Description/Particulars, Quantity, Price per Quantity, Total.
- Compute for the taxes incurred for the transaction.
- Compute for the Grand Total.
- Give the invoice to the client.

What is an Invoice?
An invoice is more than just a piece of paper or a digital document—it’s a crucial part of your business operations. It includes the following key components:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for each invoice.
- Date: The date the invoice is issued.
- Seller’s Information: Your business name, address, and contact details.
- Buyer’s Information: The customer’s name, address, and contact details.
- Description: An itemized list of the products or services provided.
- Total Amount: The total amount due, including any taxes or discounts.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on how and when the payment should be made.
What are the Contents of an Invoice?
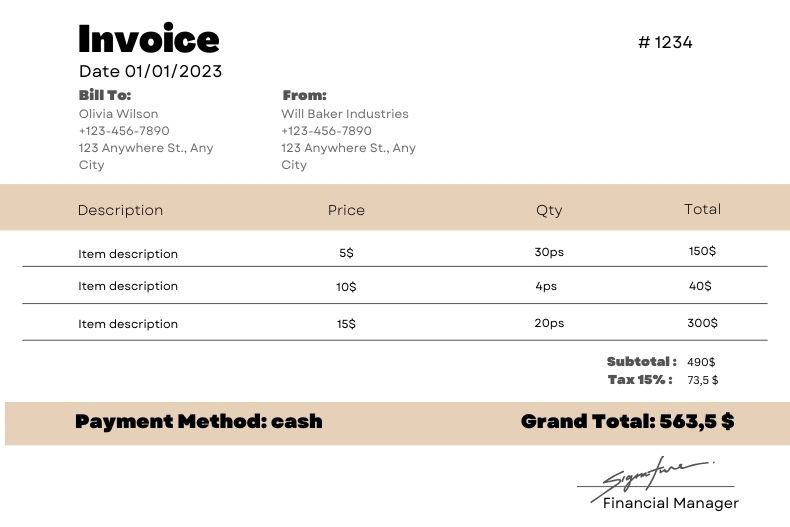
Understanding the key components of an invoice helps ensure you include all necessary information. Here’s a closer look:
- Header: Clearly label the document as an “Invoice” at the top.
- Contact Information: Include both your contact details and those of your customer. The customer’s name, address, and contact details are usually printed on the topmost portion of the invoice.
- Invoice Date and Number: Essential for tracking and record-keeping.The date of the invoice indicates the date when the goods were delivered or the services were made. The invoice number is usually found on the top of the invoice. It usually starts with the number one and moves in ascending order.
- Itemized List: Detail each product or service provided, including quantities and prices. Description/Particulars indicate the specific item or service rendered, the more specific, the better. Quantity indicates how many of a specific good was bought or how many times a specific service was rendered. Price per Quantity indicates the price for each specific good bought or each specific service rendered. Total is the amount for the specific good or specific service rendered. To get this amount, just multiply the quantity of the specific item or service rendered by the price per quantity of the specific good or service rendered. The Description/Particulars, Quantity, Price per Quantity, and Total is usually placed in a table format to make it easier to read and for faster computation.
- Subtotal, Taxes, and Total: Break down the costs, showing any applicable taxes and the final total. Breakdown of taxes are the taxes added to the transaction through the sale of goods or service rendered. Taxes involved usually vary depending on the city, state, or country. Grand Total is the sum of all items purchased or service rendered inclusive of the taxes involved. It is the total amount payable by the customer to the supplier for the transaction.
- Payment Instructions: Specify how your customer can pay you (e.g., bank transfer, credit card, PayPal).
- Terms and Conditions: Include any relevant terms, such as payment due date, late fees, and return policies.
Although there is no specific format for the invoice, if your business is in the importation of foreign goods, the US Customs and Border Protection has certain requirements and criteria for the commercial invoice. Another important thing to take note of is the sales tax, which varies from state to state.
Now that you’ve got the basic details covered, the next step would be actually filling out an invoice form.
4. How to Create an Invoice?
Creating an invoice doesn’t have to be complicated. Follow these steps to create an effective invoice:
Step 1: Choose an Invoice Template
Using an invoice template is a great way to start. Many accounting software and online tools offer customizable templates. Choose one that fits your business style and branding.
Step 2: Fill in Your Information
Add your business name, address, and contact details to the template. Make sure this information is accurate and up-to-date.
Step 3: Add Customer Information
Include your customer’s name, address, and contact details. Double-check this information to avoid any delays in payment.
Step 4: Assign an Invoice Number
Each invoice should have a unique number for tracking purposes. This helps you stay organized and makes it easier to reference specific invoices in the future.
Step 5: List Products or Services
Provide a detailed, itemized list of the products or services you provided. Include quantities, unit prices, and any applicable taxes or discounts.
Step 6: Calculate the Total Amount
Add up the costs to get the subtotal. Then, include any taxes and subtract any discounts to get the final total amount due.
Step 7: Include Payment Terms
Specify how and when the payment should be made. Include details such as payment methods accepted and the due date.
Step 8: Review and Send
Double-check all the information for accuracy. Once everything looks good, send the invoice to your customer. Many businesses send invoices via email, but you can also mail a physical copy if needed.
Why are Invoices Important?
Ensuring Timely Payments
Invoices play a critical role in ensuring you get paid on time. By providing a clear and professional document, you set the expectation for prompt payment.
Legal and Financial Record-Keeping
Invoices are essential for legal and financial record-keeping. They provide a paper trail for your transactions, which is invaluable during tax season or if any disputes arise.
Professionalism in Business Transactions
Sending a well-crafted invoice demonstrates professionalism and helps build trust with your customers. It shows that you take your business seriously and value proper documentation.
Best Practices for Invoicing
Follow these best practices to make your invoicing process smoother and more efficient:
- Send Invoices Promptly. Send your invoices as soon as possible after providing the product or service. The sooner you send the invoice, the sooner you’ll get paid.
- Be Clear and Concise. Keep your invoices clear and concise. Avoid unnecessary jargon and ensure all essential information is easy to find.
- Use Invoicing Software. Consider using invoicing software to streamline the process. These tools can help you create, send, and track invoices more efficiently.
- Follow Up on Overdue Payments. Don’t hesitate to follow up if a payment is overdue. A friendly reminder can go a long way in ensuring you get paid on time.
- Keep Records. Maintain detailed records of all your invoices. This will help you stay organized and provide a paper trail for your transactions.
How to spot a dummy invoice?
Here’s a table summarizing the differences between an invoice and a dummy invoice:
| Feature | Invoice | Dummy Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal, official document requesting payment for goods/services provided. | A preliminary bill of sale providing an estimate of costs before the actual transaction. |
| Legally Binding | Yes, it is a legal document that can be enforced in court. | No, it is not legally binding. |
| Detail Level | Detailed and final, including invoice number, date, seller and buyer info, item description, quantities, prices, total amount, and payment terms. | Preliminary and estimated information, including prices, quantities, and potential costs. |
| Primary Purpose | To request payment from the buyer for goods/services already provided. | To give the buyer an idea of potential costs and terms before the transaction. |
| Usage | Used for actual billing and payment collection. | Used for quotations, customs declarations, and preliminary discussions. |
| Example | A freelancer sends an invoice for completed project work, detailing the project, hours worked, and total fee. | An electronics supplier sends a dummy invoice to a retailer with estimated prices and quantities for an order. |
| Accounting and Tax Records | Essential for bookkeeping, accounting, and tax purposes. | Not used for official accounting records, mainly for planning and estimates. |
| Commonly Known As | Invoice | Proforma invoice |
This table provides a clear comparison of the key features and purposes of invoices and dummy
Conclusion
Invoicing might seem like a tedious task, but it’s a vital part of running a successful business. By understanding what an invoice is, why it’s important, and how to create one, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the art of invoicing. Remember to use an invoice template to make the process easier, and follow best practices to ensure you get paid on time. Happy invoicing!